Are you frustrated by your computer slow to boot? A slow boot can be a major inconvenience, causing delays and hampering productivity. This comprehensive guide will explore the reasons behind a slow computer boot and provide actionable solutions to optimize the startup process. From optimizing startup programs to optimizing system settings, we have you covered. In this guide, you can reduce your computer’s boot time and enjoy a faster, more efficient computing experience. Say goodbye to waiting and regain control over your computer’s startup speed with our expert tips and tricks.
1. Fix Computer slow to boot: Disable Unneeded Startup Programs
Too many apps launching at boot can slow things down. Disable unneeded programs in Task Manager to fix computer slow to boot issue.
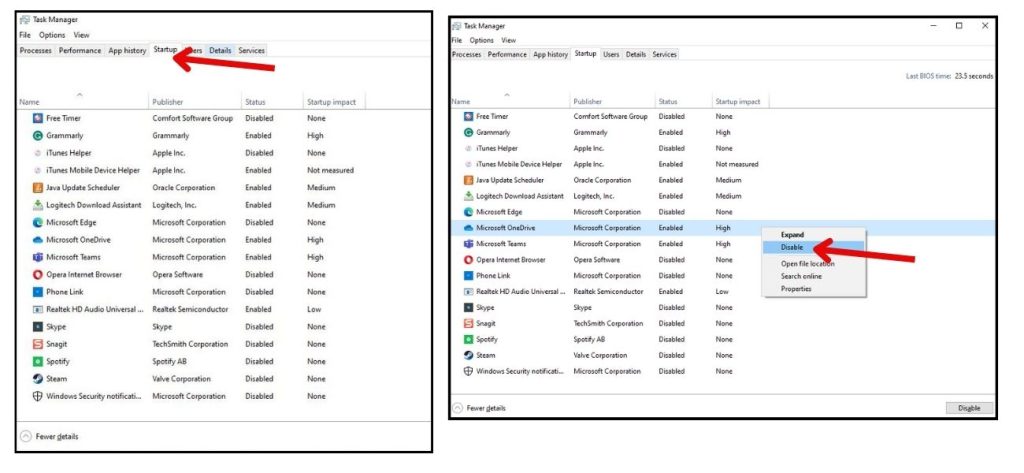
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Click the Startup tab.
- Right click programs with a high impact and select Disable.
This prevents them from automatically launching at startup.
2. Update Outdated Drivers
Is your Windows 10 computer taking ages to boot up, accompanied by frustrating Wi-Fi connectivity problems? One effective troubleshooting method to address Computer slow to boot issue is updating outdated drivers.
Outdated drivers, especially for graphics cards, can significantly slow down boot times.
Open Device Manager, right-click your display adapter and select Update driver. Or use a driver update utility to handle this automatically.
Be sure to restart after updating drivers.
3. Run an SFC Scan
The System File Checker scans Windows for corrupted system files and replaces them. This can fix files responsible for slowing down the boot process.
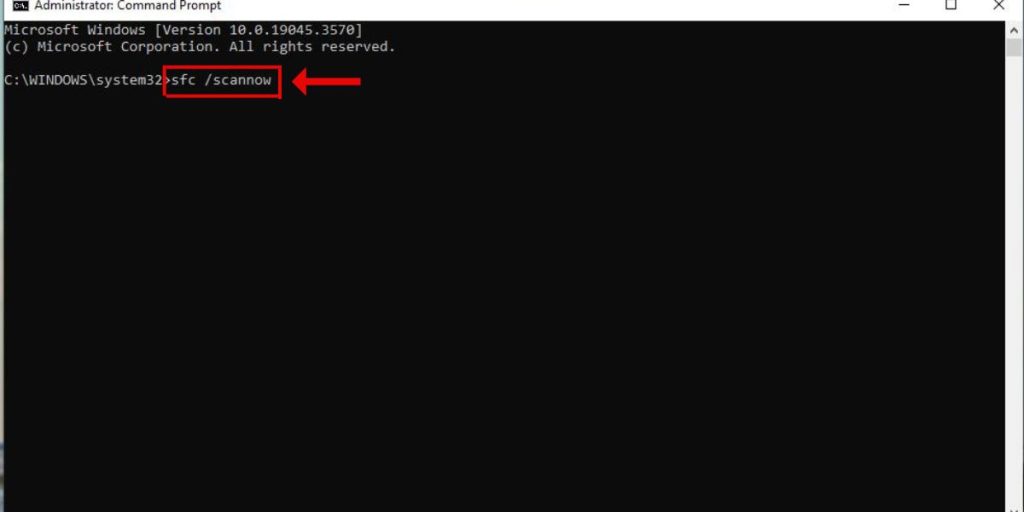
To run an SFC scan:
- Open an elevated Command Prompt.
- Type “sfc /scannow” and hit Enter.
- Restart your PC once completed.
4. Adjust Virtual Memory Settings
If Windows changes your paging file size incorrectly, it can impede startup. Check the recommended and current sizes in Advanced system settings. Make sure they match by choosing Custom Size and entering the recommended values.
5. Perform a Clean Boot
Start your PC in a clean boot state, disables all non-Microsoft services. If boot is faster, a third-party app is likely the culprit.
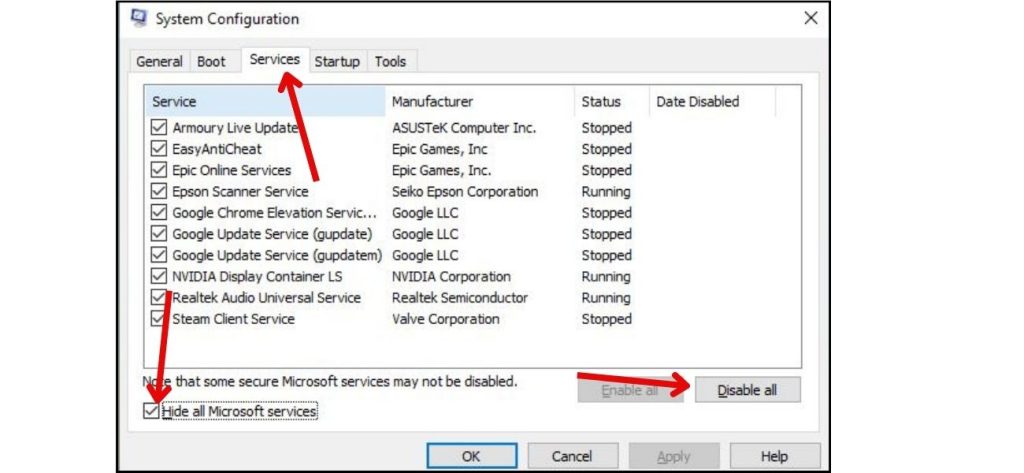
To clean boot:
- Open msconfig
- Go to Services and check “Hide Microsoft services.”
- Click “Disable all,” then restart.
6. Check Drive Health
Corrupted areas on a failing hard drive or SSD can slow down booting. Check your boot drive’s health with the manufacturer’s utility. Consider replacing the drive if needed.
7. Reset Windows
A computer slow to boot can be caused by various factors, such as software conflicts, driver problems, or corrupted system files. By performing a reset, you can effectively eliminate these underlying issues and restore your computer’s performance to its optimal state.
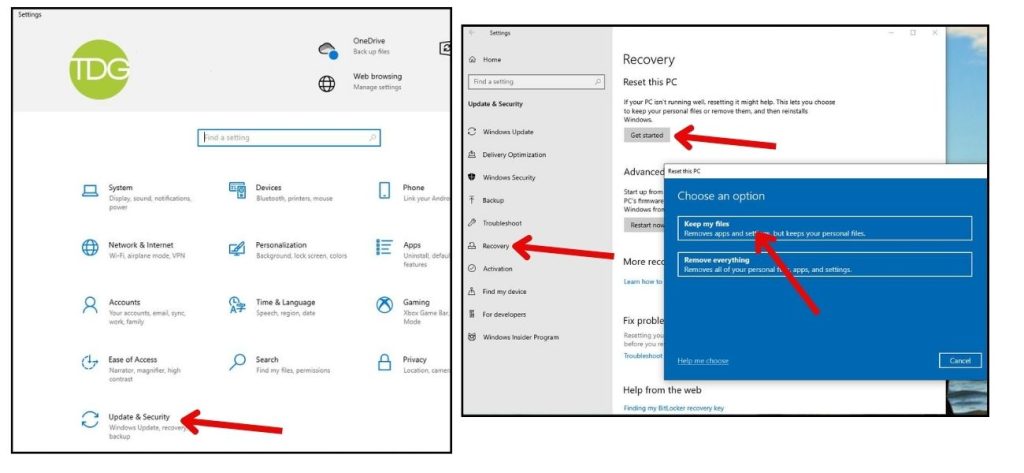
As a last resort, reset your PC by going to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery> Reset this PC. Choose to keep personal files if possible. Resetting will reinstall Windows and fix many issues.
8. Upgrade to an SSD
If you’re booting from a hard disk drive, upgrading to a solid state drive can drastically improve startup time along with overall system speed. Though pricier, an SSD is one of the best upgrades you can make.