If your CPU fan has stopped spinning, your computer is at risk of overheating and serious damage. A non-working CPU fan indicates an underlying issue that needs to be addressed immediately.
Don’t panic – there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to get your CPU fan spinning again. Here are the top 10 methods to fix a CPU fan not spinning issue:
1. Restart Your Computer
A simple reboot can get your CPU fan spinning again. The restart clears any software glitches and sends a jolt of power through the motherboard components.
Here are the steps to restart your computer:
- Close any open programs and save your work.
- Click on the Start menu and select Power.
- Choose Restart from the menu.
- Wait for your computer to fully shut down.
- After a few seconds, press the power button to turn your computer back on.
- Once restarted, check if the CPU fan is now spinning properly.
A restart fixes the no-spin issue in many cases by resetting components.
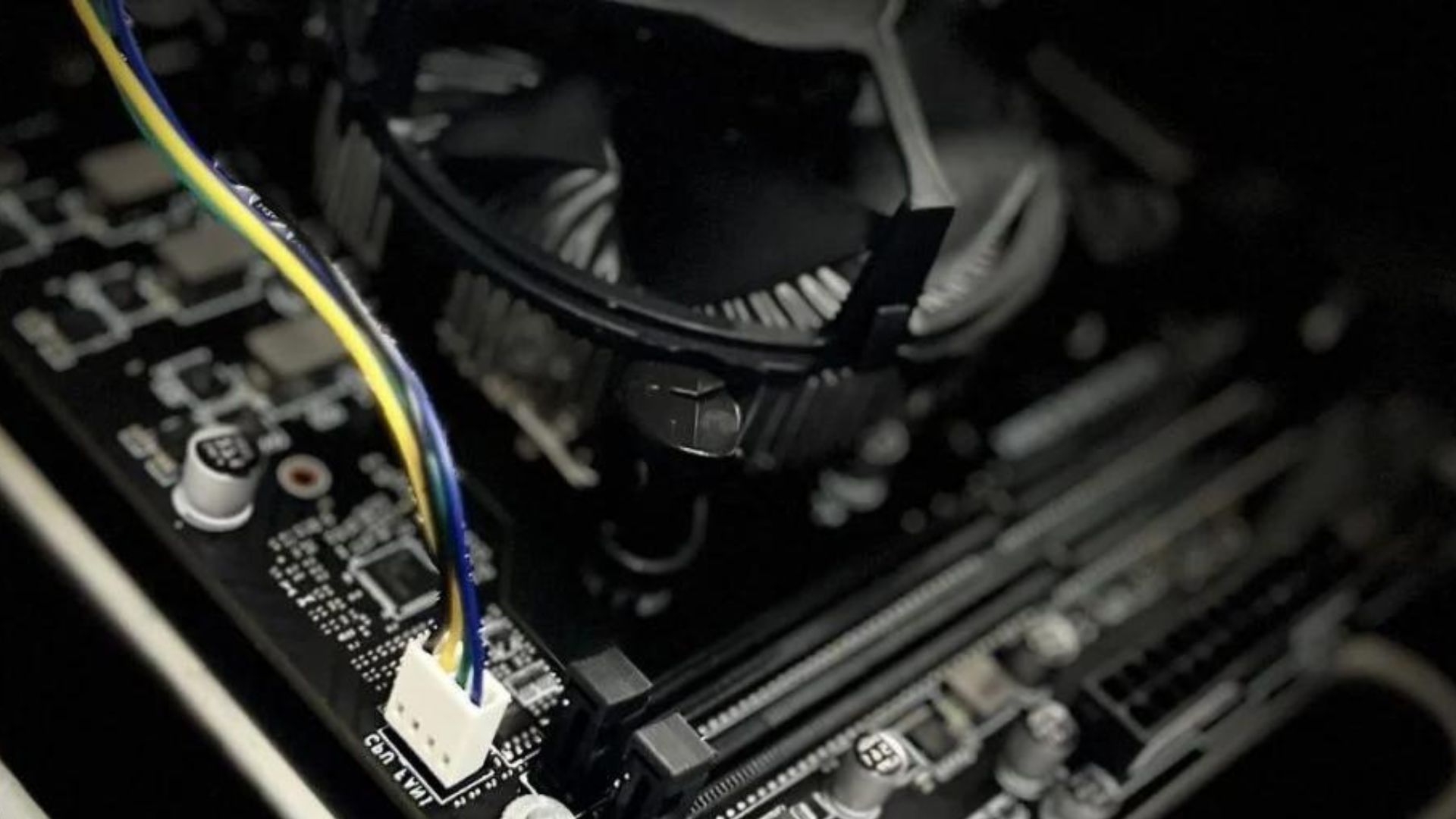
2. Check CPU Fan Connections
Make sure the CPU fan cable is properly plugged into the CPU_FAN header on the motherboard. Reseat the connection or try a different fan header if needed. Faulty connections are a common reason for CPU fan failures.
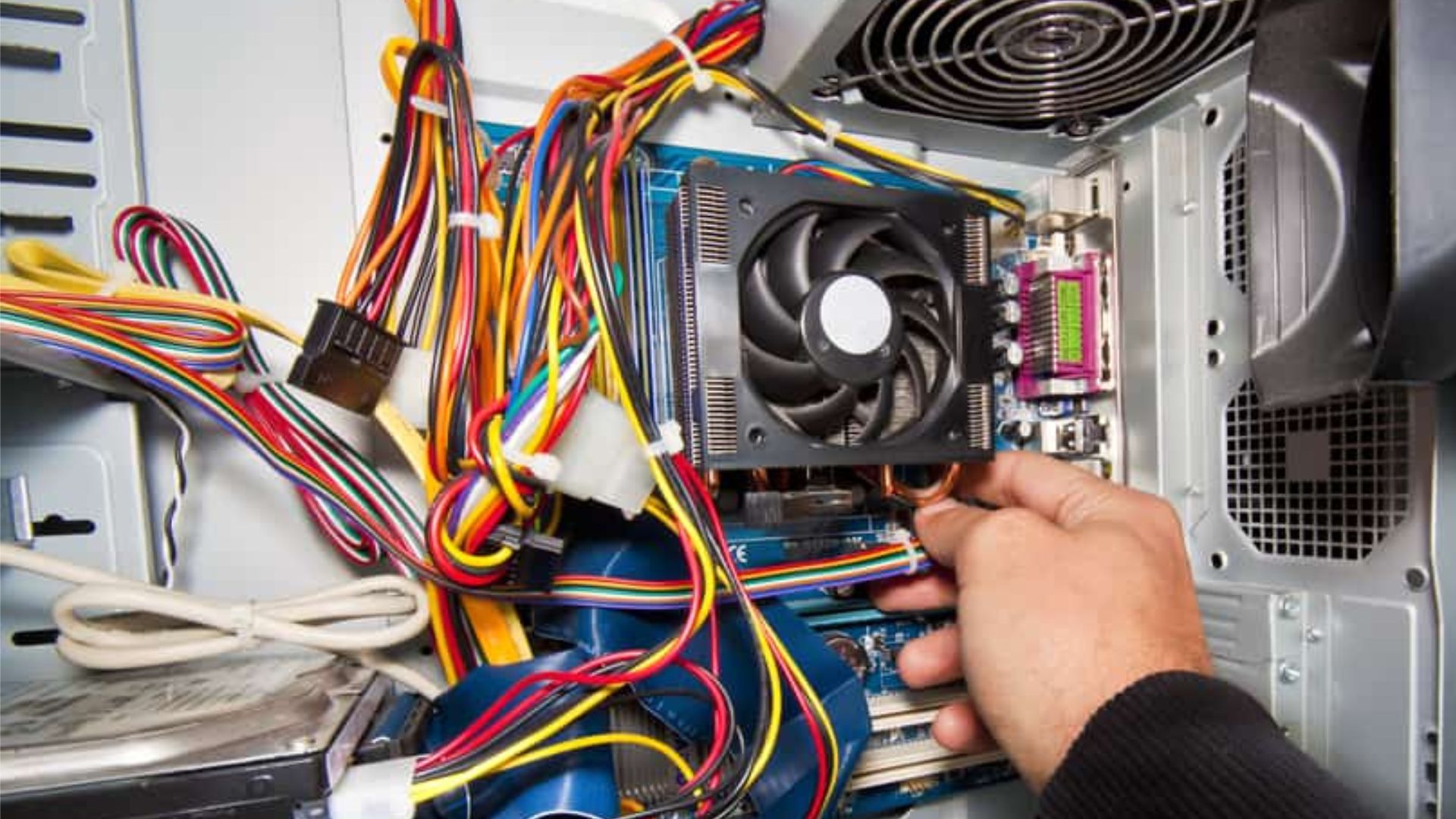

Also check that no wires or cables are obstructing the fan blades. The fans have low torque and can jam easily.
Follow these steps to check the CPU fan connections:
- Power off your computer and unplug the power cable.
- Open the PC case and locate the CPU fan cable.
- Check that the cable is firmly inserted into the CPU_FAN header on the motherboard.
- If loose, press down firmly to reseat the connection.
- Inspect nearby wires and cables to ensure they don’t touch or obstruct the fan blades. Tie back if needed.
- Try plugging the CPU fan into another chassis fan header to test spin functionality.
- Close the PC case, reconnect power cable, and power on the computer.
- Verify the CPU fan is now spinning properly.
3. Clean Dust From the CPU Fan
Over time, dust buildup can clog the CPU fan and prevent smooth spinning. Use compressed air to blast dust away and ensure the fan spins freely.
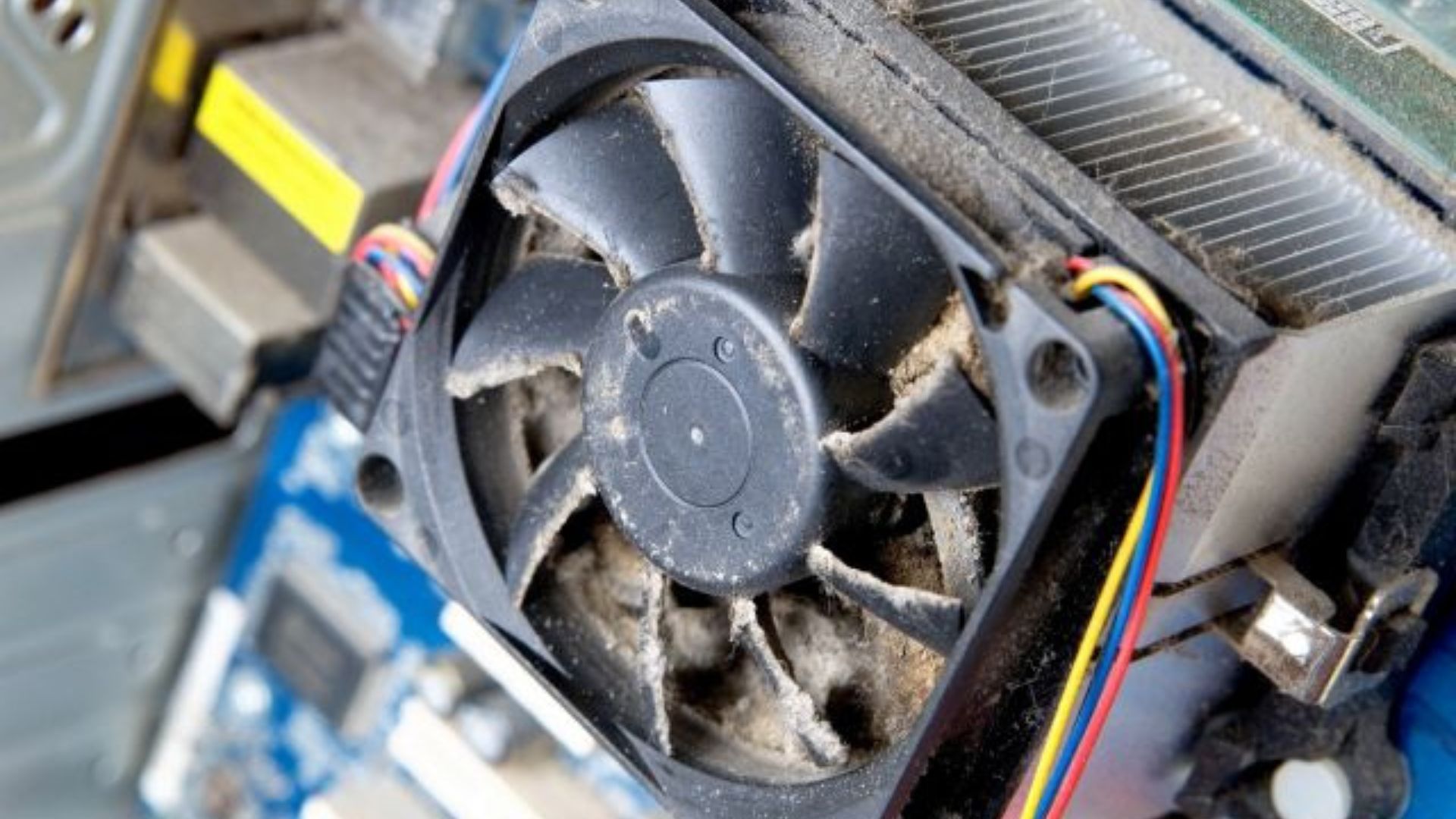

Avoid touching the fan blades while cleaning. You may need to remove the fan to thoroughly clean dust in hard to reach areas.
Follow these steps:
- Power off the computer and open the case.
- Locate the CPU fan and inspect for dust buildup.
- Hold the fan blade lightly and try spinning with finger. It should move easily.
- If dusty, use short bursts of compressed air to dislodge dust from fan.
- Clean any dust from the heatsink fins surrounding the fan as well.
- To deep clean, unscrew and remove the fan from the motherboard.
- Use compressed air to blow away all dust from the fan.
- Wipe down with lint-free cloth if needed. Avoid bending fan blades.
- Reattach the cleaned CPU fan and power on to check for proper spinning.
4. Update Motherboard BIOS
An outdated or buggy BIOS can send incorrect signals to control the CPU fan speed. Updating to the latest stable BIOS version often fixes fan control issues.
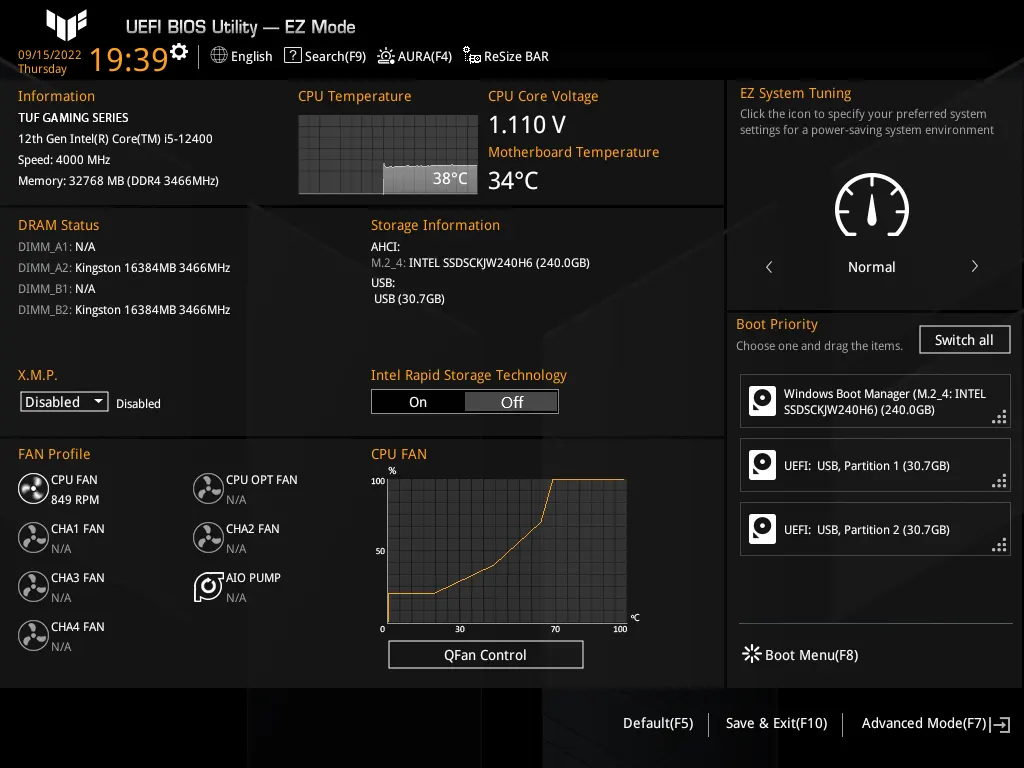
Consult your motherboard manual on how to access and update the BIOS. Take care not to interrupt the update process once started.
Here is how to update the motherboard BIOS:
- Note your current BIOS version in the Setup utility.
- Go to the manufacturer website and find the latest BIOS update for your motherboard model.
- Download the BIOS .zip file to your computer and extract it.
- Copy the BIOS .bin file from your extracted folder to a USB flash drive.
- Reboot into BIOS setup and select the BIOS update option.
- Locate the flash drive and select the .bin file. Follow prompts to flash BIOS.
- Reboot once BIOS update completes. The CPU fan should now work if a buggy BIOS was the issue.
5. Reset BIOS to Default Settings
Reset the BIOS to clear any corrupted settings that could be disrupting the CPU fan operation. The reset will restore BIOS options to their default values.
Access the BIOS on boot, load defaults, save changes and exit. The CPU fan should now work if misconfiguration was the cause.
To reset the BIOS:
- Reboot your computer and press the BIOS key (F2, F10, Del) to enter Setup.
- Navigate to the Exit menu.
- Select the option to Load Optimized Defaults.
- Press F10 to save changes and exit BIOS.
- In the confirmation prompt, select Yes to load defaults.
- The computer will reboot with reset BIOS. Check if CPU fan now spins properly.
6. Check Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Insufficient power from a failing PSU can cause CPU fans to not spin. Test with a known-good PSU to isolate the issue. Replace the PSU if determined to be faulty.
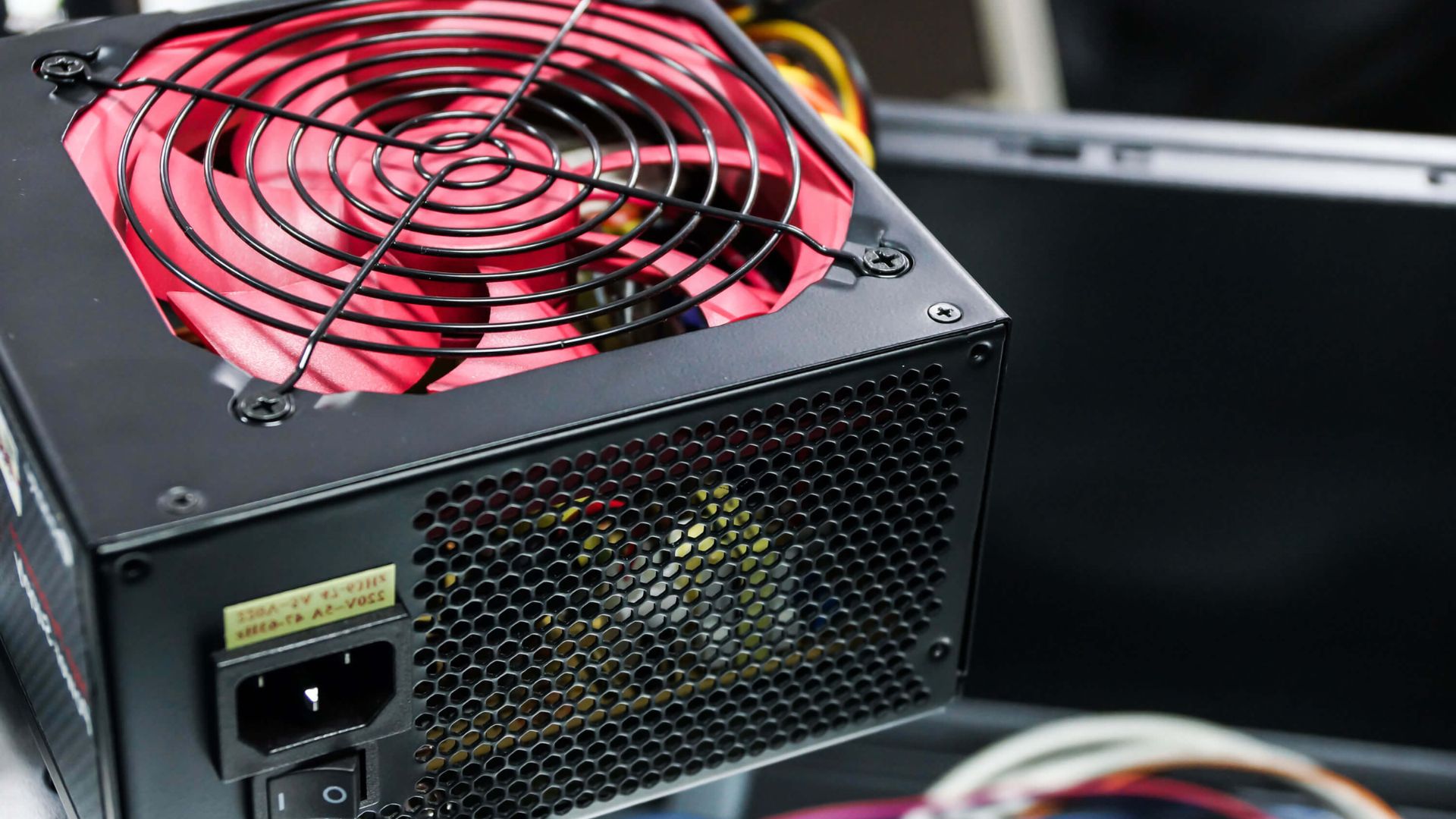

Use PC power supply calculators to ensure your PSU can provide ample power to all components. Always allow some headroom over total system power draw.
To check the PSU:
- Power off and unplug the computer.
- Unmount the PSU from the case and disconnect all cables.
- Use a multimeter to test voltage levels on PSU cables.
- Ensure the 12V and 5V rails show correct values. A variance of +/- 5% is acceptable.
- If voltages are unstable or outside specs, the PSU is likely faulty.
- Replace with a high-quality PSU appropriately sized for your system.
- Retest CPU fan operation after replacing the faulty power supply.
7. Replace Faulty CPU Fan
If the above steps don’t get your CPU fan spinning, the fan itself has likely failed. Replacing the CPU fan with a new one of the same model is the fix.
Match the fan’s voltage rating, pin type, mounting holes, and dimensions to avoid compatibility issues. Consult your motherboard or CPU manual for correct fan specifications.
Follow these steps to replace a dead CPU fan:
- Power off and open up your computer case.
- Locate and remove the CPU fan power connector from the motherboard header.
- Unscrew the mounting screws to detach the fan from the CPU heatsink.
- Note the fan specifications – size, power rating, connector type, etc.
- Purchase a new replacement fan with identical specifications.
- Mount the new fan onto the heatsink using the screws. Ensure it is securely attached.
- Connect the fan cable to the CPU_FAN motherboard header.
- Close the case and power on the PC. Verify the new fan works properly.
8. Check for Faulty Motherboard
Try testing with a known working CPU fan. If the fan still doesn’t spin, suspect a motherboard failure. The board might have a fried fan control circuit.
Replacing a failed motherboard can be expensive. Weigh the cost vs buying a new system. Also check if the motherboard is still under warranty for free repairs.
To test for a faulty motherboard:
- Replace the non-working CPU fan with a known good fan.
- Ensure you properly connect the replacement fan to the CPU_FAN header.
- Power on the computer and check if new fan spins normally.
- If the known-good fan still doesn’t spin, the motherboard is likely faulty.
- Consider sending to manufacturer for repair if under warranty.
- Otherwise, replacement cost may outweigh a new system altogether.
9. Verify Thermal Paste Application
Improper thermal paste application between the CPU and cooler can cause overheating and fan failures. Check for proper paste coverage and reapply if needed.
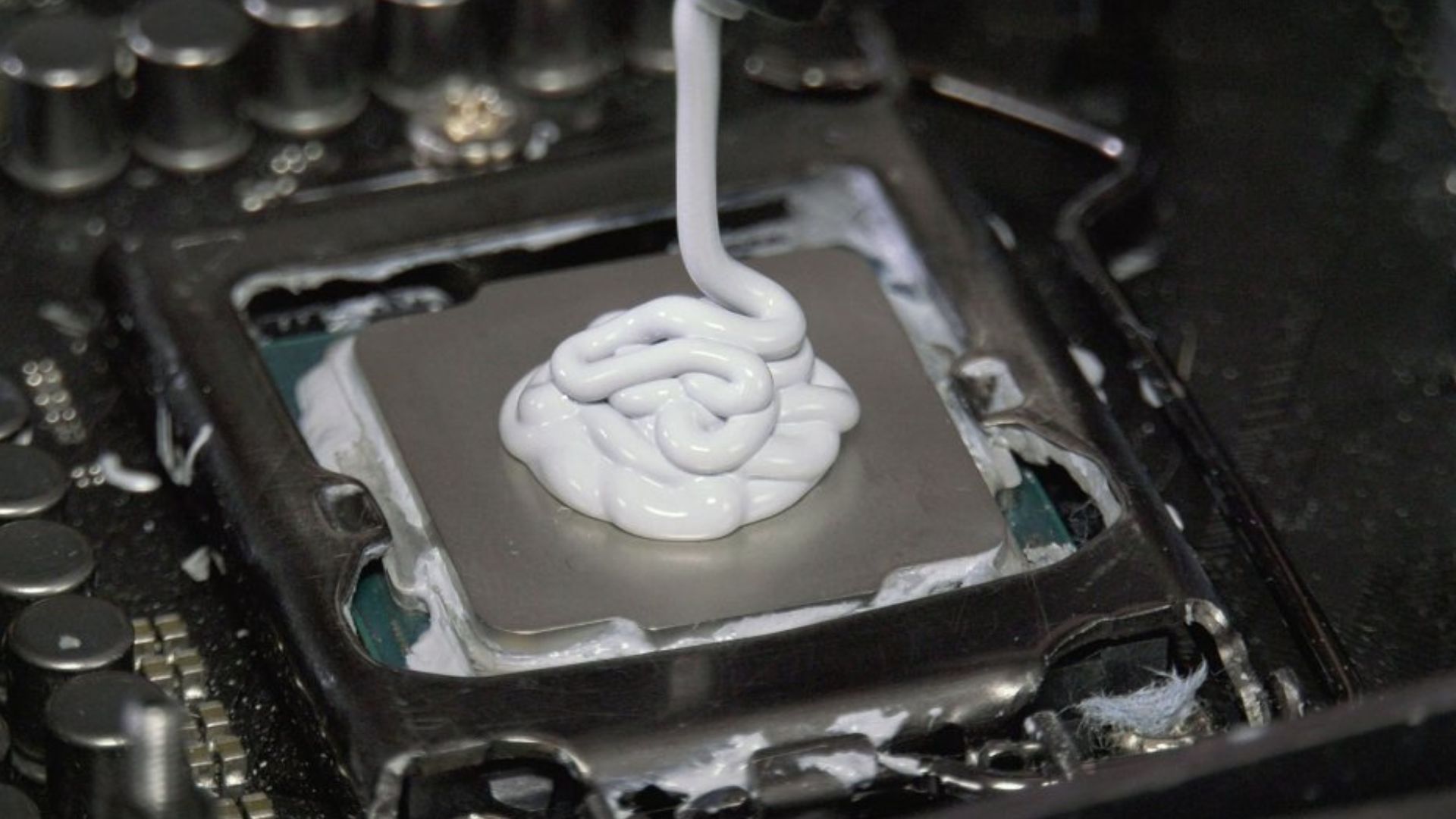

Use rice-grain size dots or thin uniform layer per paste instructions. Spread paste evenly across CPU top and cooler bottom for optimal heat transfer.
Follow these steps to reapply thermal paste:
- Power off and open the computer case.
- Detach the CPU fan and heatsink from the motherboard.
- Carefully wipe away any existing dried paste from CPU and heatsink.
- Apply fresh paste using dot or spread method based on paste type.
- Ensure the layer is thin and evenly covers the CPU surface.
- Re-mount the heatsink and attach the CPU fan.
- Boot the computer and check that improved cooling allows the CPU fan to work.
10. Monitor CPU Temperatures
Use CPU monitoring software to check temperature readings during system load. Thermal throttling and fan stoppage can occur if temperatures exceed safe limits.
High temperatures indicate cooling issues that need addressing. Upgrade CPU cooler, improve case airflow, clean fans, replace thermal paste to lower temps.
To check CPU temperatures:
- Download an app like Speccy or HWInfo to monitor CPU temps.
- Run intensive tasks like gaming or video editing to simulate heavy load.
- Observe the core temperature readings under load using your app.
- If temps consistently exceed 90°C, you likely have cooling issues.
- Upgrade CPU cooler, add intake/exhaust fans, reapply thermal paste to lower temps.
- Resolve cooling issues to prevent potential CPU overheating and fan failures.
Avoid prolonged computer use if CPU fan doesn’t work. The cumulative overheating damage can be severe. Implement the applicable fix to get the essential cooling for normal operations. With persistence and methodically trying each solution, you can get the uncooperative CPU fan spinning again.